Example 4 - Stepping Analysis of a Synchronous Machine
Goal: Perform magnetostatic stepping over different rotor angles, for a synchronous machine.
Result: Different waveform plots, flux density plots, and a structure of important performance indicators.
Prequisites
Making sure that a model has already been initialized.
if ~exist('motor', 'var')
Example_01_Setting_up_a_Model;
close all;
end
gmsh path E:\Software\Work\gmsh-4.11.1\ loaded from preference group 'emdtool'
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
motor 1x1 8 RFmodel
Background
This example analyses a synchronous (PM) machine at a single operating point (constant rpm, sinusoidal phase currents), using what is called ‘static analysis’ in EMDtool. Here, ‘static’ refers to the fact that that eddy currents and similar damping effects are ignored, otherwise it works very much like what one would expect from a constant-rpm transient simulation with imposed current waveforms.
Initializations
We again begin by instantiating a MagneticsProblem object
problem = MagneticsProblem.new(motor);
and then specify the operating point to analyse
rpm = 3000; %rpm
Jrms = 10e6; %rms current density
pole_angle = pi/180 * 90; %Note: 90 degrees corresponds to id = 0
Finally, to keep things fast, we only analyse one sixth of the electrical period (enough for typical distributed-wound machines in ideal steady-state) using a moderate 11 steps
angles = linspace(0, 2*pi/6, 11); %electrical angles to step through
Running the analysis
Setting the excitation
First, we compute the current waveforms corresponding to our desired rms current, pole angle, and number of steps:
phase_circuit = stator.winding;
spec = stator.winding_spec;
Ipeak = sqrt(2)*Jrms * phase_circuit.conductor_area_per_turn_and_coil();
Is = spec.xy(Ipeak*[cos(pole_angle); sin(pole_angle)], angles);
Next, we set the just-computed waveforms as the excitation for the stator winding, exactly in the same fashion as we did in the torque curve example:
phase_circuit.set_source('uniform coil current', Is);
Simulation parameters
Next, we define the simulation parameters. For static stepping, the only crucial parameters are typically the frequency and the (mechanical) rotor angles to step through:
%parameters
pars = SimulationParameters('f', rpm/60*dim.p, 'rotorAngle', angles/dim.p, ...
'silent', ~true);
Solution
Next, the problem is solved.
stepping_solution = problem.solve_static(pars);
Computing step/case 1 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 1.
Newton step 2, relative residual 18.043.
Relaxation automatically set to 0.9
Newton step 3, relative residual 3.3023.
Newton step 4, relative residual 1.2495.
Newton step 5, relative residual 0.19708.
Newton step 6, relative residual 0.059244.
Newton step 7, relative residual 0.021485.
Newton step 8, relative residual 0.0069899.
Newton step 9, relative residual 0.0021695.
Newton step 10, relative residual 0.00094776.
Newton step 11, relative residual 0.00049132.
Newton step 12, relative residual 0.00020549.
Newton step 13, relative residual 7.0589e-05.
Newton step 14, relative residual 2.1045e-05.
Newton step 15, relative residual 7.1874e-06.
Newton step 16, relative residual 1.6706e-07.
Computing step/case 2 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.1616.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.029239.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0017543.
Newton step 4, relative residual 7.7909e-05.
Newton step 5, relative residual 3.532e-06.
Newton step 6, relative residual 2.6741e-08.
Computing step/case 3 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0937.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.014582.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.00062131.
Newton step 4, relative residual 5.0827e-05.
Newton step 5, relative residual 3.7208e-06.
Newton step 6, relative residual 8.4766e-08.
Computing step/case 4 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0544.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.012704.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0014285.
Newton step 4, relative residual 7.5252e-05.
Newton step 5, relative residual 1.4031e-06.
Newton step 6, relative residual 3.8154e-08.
Computing step/case 5 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0768.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.0071109.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.00034649.
Newton step 4, relative residual 1.8286e-05.
Newton step 5, relative residual 4.0907e-07.
Computing step/case 6 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.1055.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.01162.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0018736.
Newton step 4, relative residual 0.00023072.
Newton step 5, relative residual 7.4157e-06.
Newton step 6, relative residual 1.962e-07.
Computing step/case 7 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0779.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.053552.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0052944.
Newton step 4, relative residual 0.00033058.
Newton step 5, relative residual 1.2514e-05.
Newton step 6, relative residual 2.355e-07.
Computing step/case 8 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0271.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.020056.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.00066775.
Newton step 4, relative residual 8.8412e-05.
Newton step 5, relative residual 1.2657e-05.
Newton step 6, relative residual 8.6345e-07.
Computing step/case 9 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0173.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.08393.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.012441.
Newton step 4, relative residual 0.0039697.
Newton step 5, relative residual 0.0010366.
Newton step 6, relative residual 6.9793e-05.
Newton step 7, relative residual 1.2795e-06.
Newton step 8, relative residual 1.4703e-08.
Computing step/case 10 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.0903.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.010136.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0011861.
Newton step 4, relative residual 0.00011047.
Newton step 5, relative residual 1.5789e-05.
Newton step 6, relative residual 8.9525e-07.
Computing step/case 11 out of 11...
Newton step 1, relative residual 9.1738.
Newton step 2, relative residual 0.010179.
Newton step 3, relative residual 0.0014181.
Newton step 4, relative residual 0.00020407.
Newton step 5, relative residual 2.412e-05.
Newton step 6, relative residual 9.4879e-07.
Post-processing
Plotting
We proceed to plot the airgap flux density waveform,
figure(4); clf; hold on; box on;
motor.plot_airgap_flux_density(stepping_solution, 11)
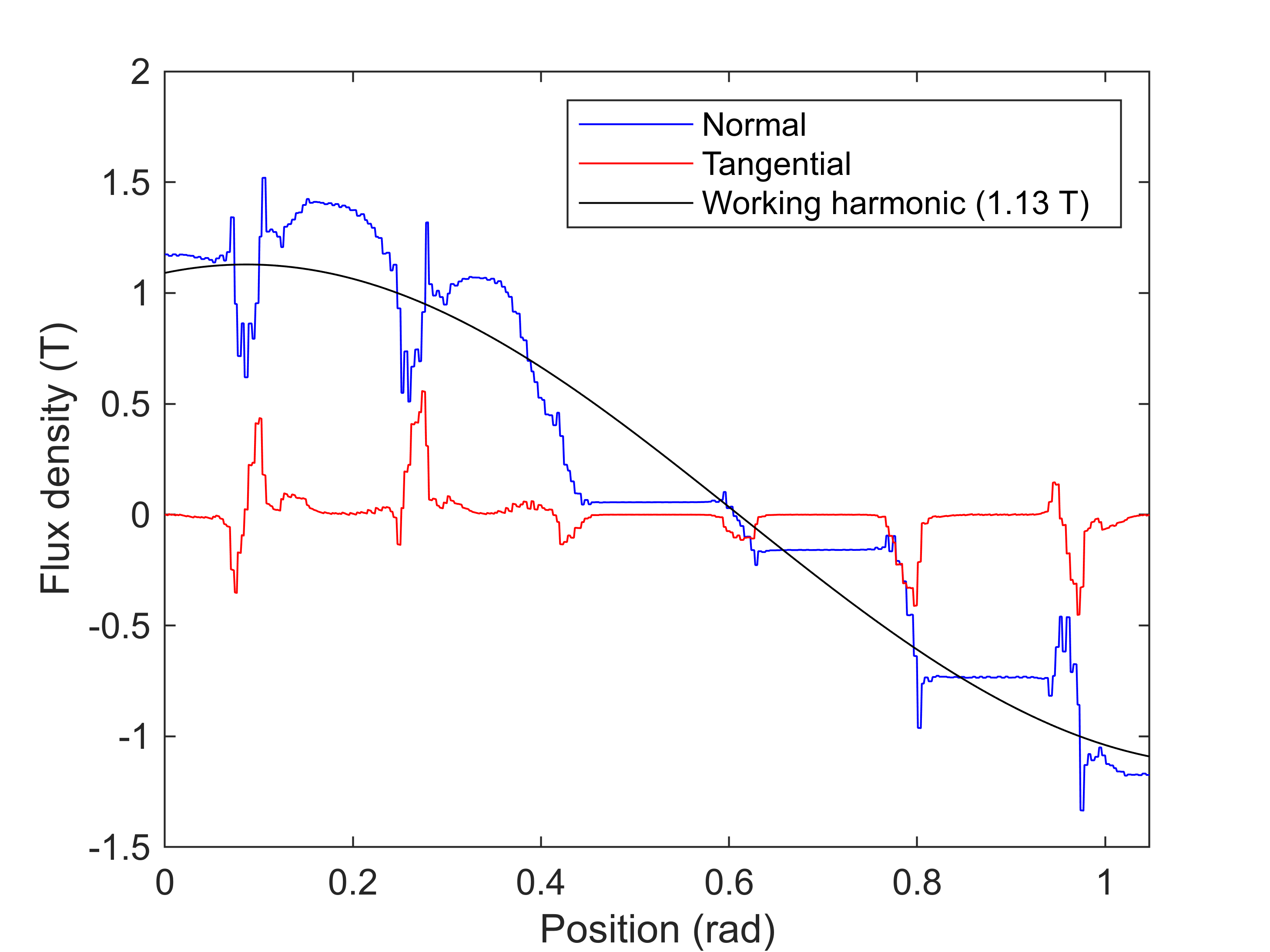
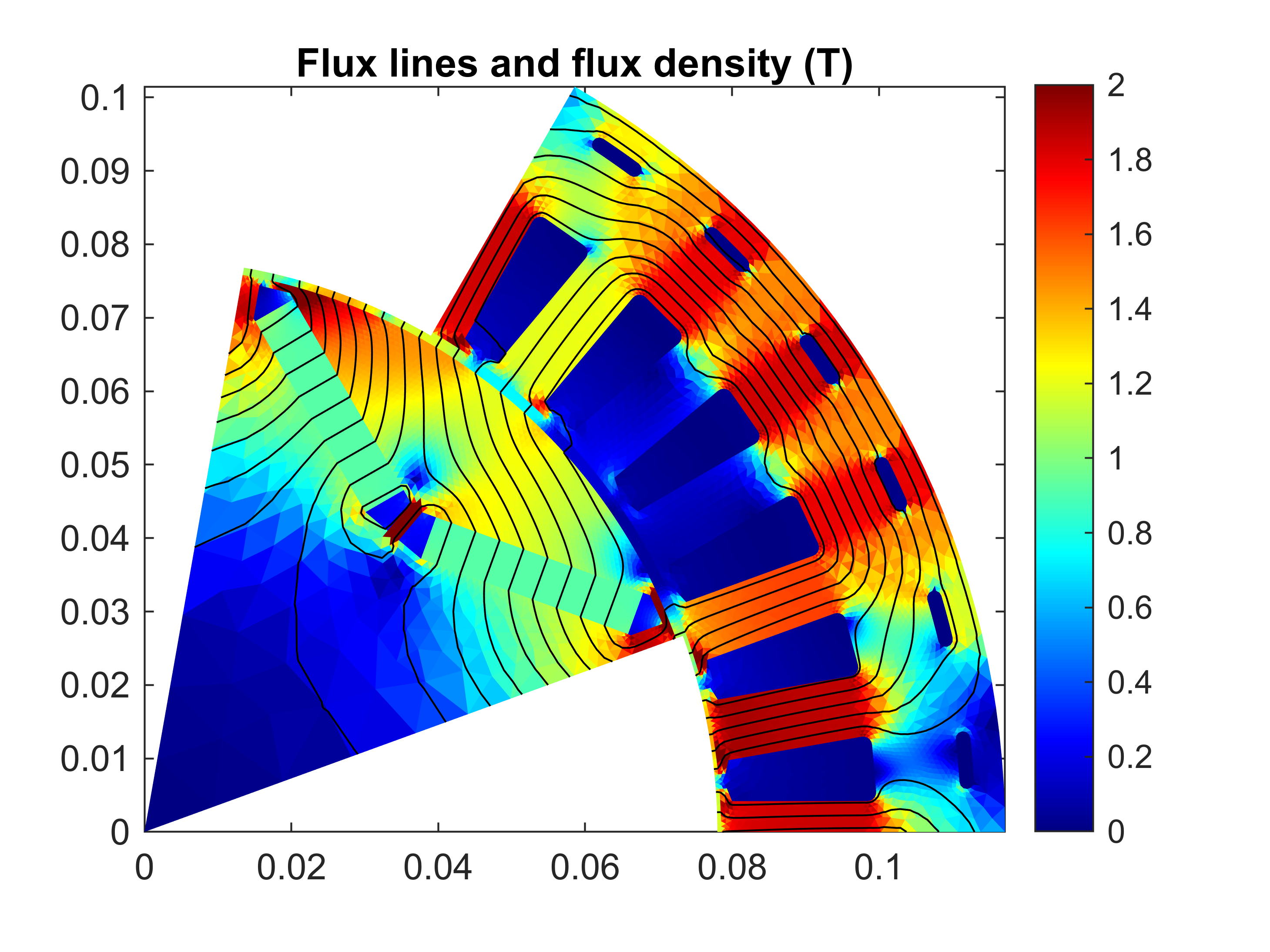
the flux density distribution at step 11,
%plotting example of flux
figure(5); clf; hold on; box on;
motor.plot_flux(stepping_solution, 11);
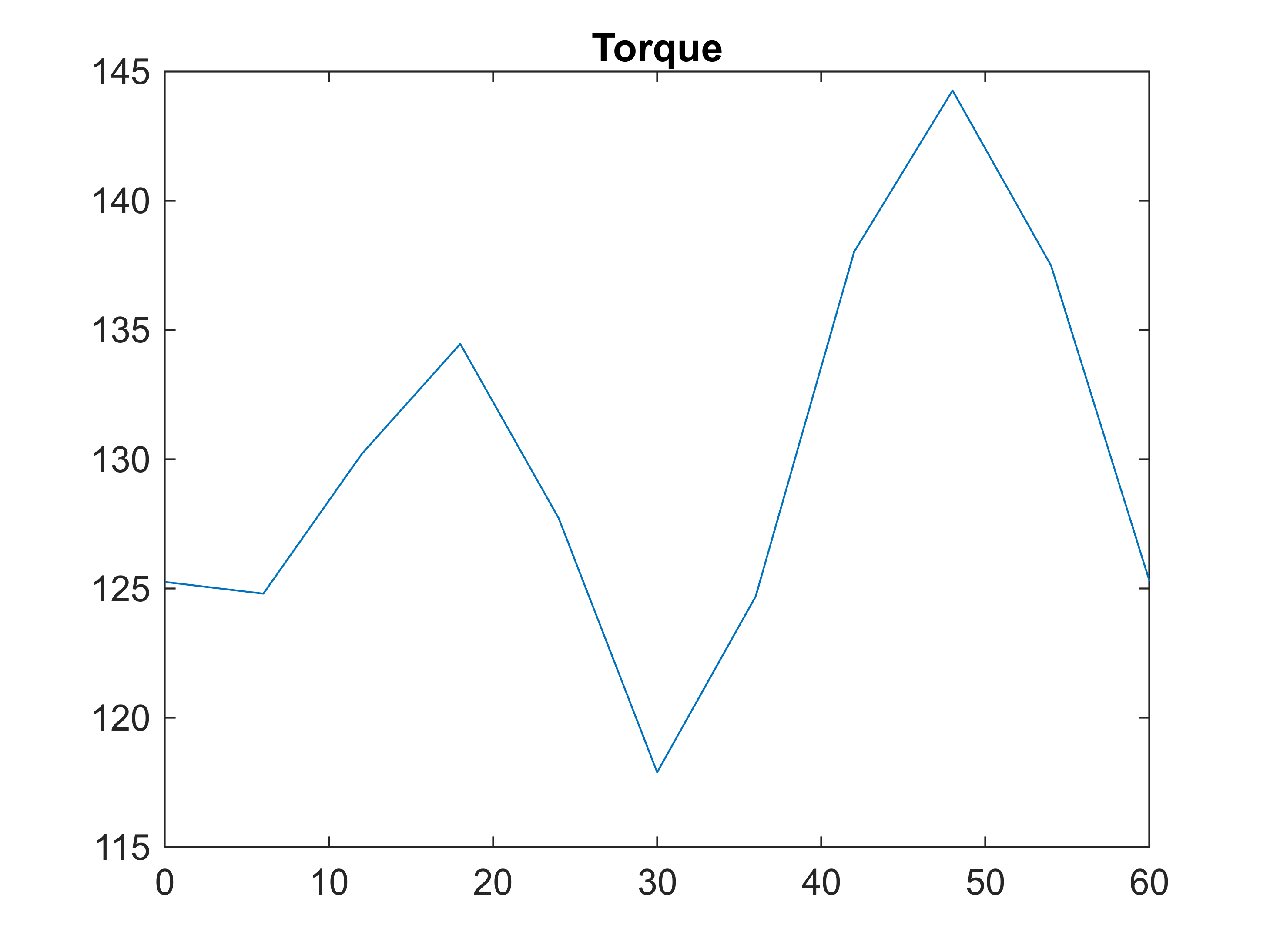
the torque waveform
%plotting torque
T = motor.compute_torque( stepping_solution );
figure(6); clf; hold on; box on; title('Torque');
plot(angles/pi*180, T);
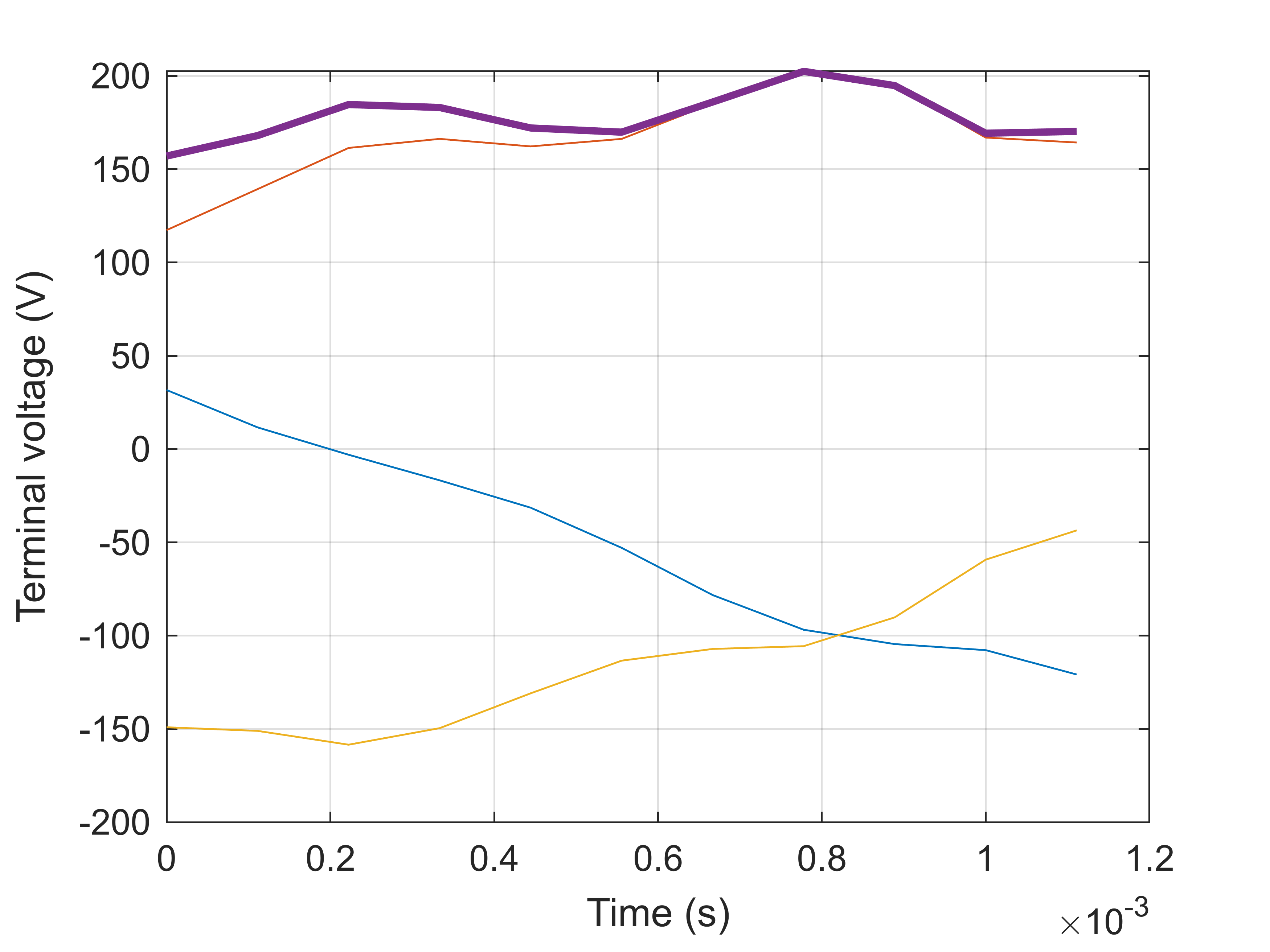
and some voltage waveforms (note that the ‘back-emf’ method returns the simply the time-derivative of the flux linkage, without differentiating whether it’s inductive or PM/field-winding related)
%voltages
voltage = phase_circuit.terminal_voltage(stepping_solution);
voltage_dq = phase_circuit.terminal_voltage( stepping_solution, 'output', 'space vector');
phase_voltage = phase_circuit.phase_bemf(stepping_solution);
phase_voltage_dq = phase_circuit.phase_voltage(stepping_solution, 'output', 'space vector');
%plotting
figure(7); clf; hold on; box on; grid on;
plot(stepping_solution.ts, voltage);
plot(stepping_solution.ts, colnorm(voltage_dq), 'linewidth', 2);
xlabel('Time (s)');
ylabel('Terminal voltage (V)');
Results summary
Finally and importantly, we compute the results summary with the MotorModelBase.results_summary method. The method returns a Matlab structure; in addition we are giving the 'verbose' argument to also display the results in the Matlab command window.
summary = motor.results_summary(stepping_solution, 'verbose', true);
Warning: The extruded block height 150 mm is less than the skin depth (17.608 mm) at 10x fundamental frequency. The results may be inaccurate. Consider running a transient simulation / setting the circuit as active.
Summary of results:
git_commit_ID : 8cced832b0ccd486ccf7bbeb18d29643f015c25c
rpm : 3000
f : 150
torque_waveform : (array)
torque_mean : 130.0088
shaft_power : 40843.4653
torque_ripple_min_to_max : 26.3679
torque_ripple_rms : 7.5695
timestamps : (array)
efficiency : 0.95693
total_losses : 1838.3056
input_power_from_power_balance : 42681.7709
input_power_from_terminal_waveforms : 42348.0453
**********************************************************
phase_circuit_data:
input_power : 42348.0453
input_power_waveform : (array)
apparent_input_power : 52594.4956
displacement_power_factor : 0.6792
I_phase_waveform : (array)
I_phase_dq : 8.141787e-14 404.7173
I_phase_rms : 286.1783
phase_advance_angle_deg : -1.4211e-14
I_terminal_waveform : (array)
I_terminal_rms : 286.1783
I_terminal_THD : 2.0206e-31 2.8878e-32 3.4654e-32
U_phase_waveform : (array)
U_phase_induced : (array)
U_phase_dq : -75.3802 69.7574
U_phase_rms : 73.4122
U1_phase_rms : 72.6233
phase_flux_linkage : (array)
U_terminal_waveform : (array)
U_terminal_rms : 127.1536
U1_terminal_rms : 125.7872
coil_current_density_rms : 10000000
supply_mode : uniform coil current
**********************************************************
total_iron_losses : 437.8727
**********************************************************
iron_loss_data:
P_total : 437.8727
P_total_time : (array)
P_hysteresis : 337.8309
P_rotor : 35.7423
P_hysteresis_rotor : 30.859
P_eddy_rotor : 4.8834
P_eddy : 100.0418
P_excess : 0
P_excess_rotor : 0
p_hysteresis_elementwise : (array)
p_eddy_elementwise : (array)
p_excess_elementwise : (array)
**********************************************************
iron_losses_per_domain:
stator_Stator_core : 402.1304
stator_Stator_slot_opening : 0
stator_Stator_winding_segment : 0
stator_Cooling_channel : 0
rotor_Core : 35.6747
rotor_Shaft : 0.067674
rotor_Air : 0
rotor_Magnet_1 : 0
rotor_Magnet_2 : 0
**********************************************************
**********************************************************
total_circuit_losses : 1400.4329
total_Phasewinding_losses : 1395.3803
**********************************************************
Phasewinding_loss_data:
conductor_loss_waveform : (array)
mean_total_losses : 1395.3803
mean_AC_losses : 0
mean_DC_losses : 1395.3803
mean_EW_losses : 653.0731
mean_conductor_losses : 40.93833 40.93833 310.9356 310.9356 345.8162 345.8162
mean_circulating_current_losses : 2.2737e-13
mean_circulating_current_losses_on_phase_level : 0
total_DC_losses : (array)
**********************************************************
total_Magnets_losses : 3.5317
**********************************************************
Magnets_loss_data:
mean_losses_per_conductor : 1.6725 1.8592
conductor_loss_waveform : (array)
**********************************************************
total_Shaft_losses : 1.5208
**********************************************************
Shaft_loss_data:
mean_losses_per_conductor : 1.5208
conductor_loss_waveform : (array)
elementwise_current_density_array : (array)
**********************************************************
NEXT UP: Example 05 Transient Analysis of Synchronous Machine